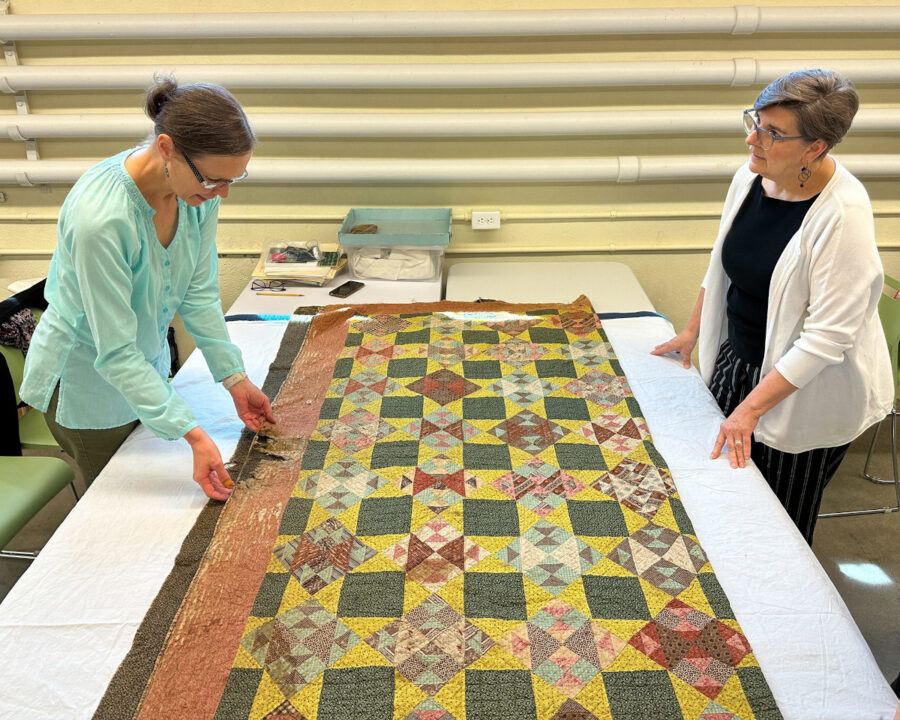
In a world where cultural shifts can be measured in minutes and miniature revolutions occur daily on social media, tracking and safeguarding our evolving culture becomes increasingly challenging. As misinformation spreads rapidly and globalization alters traditions, our collective heritage and identity face growing threats. Even tangible artifacts and artworks, concrete links to our past, are vulnerable to climate change, urban development, and cultural homogenization that erodes their significance. The urgency to conserve these invaluable pieces demands a tailored approach, one that adapts preservation techniques to the unique characteristics of each artifact and its cultural context. By doing so, we not only protect our heritage but also strengthen the cultural narratives that define our shared humanity.
Understanding the Cultural Context of Artifacts
Effective cultural heritage preservation requires acknowledging that artifacts do not exist in isolation. Each piece carries historical, traditional, and identity-based significance, making it essential to approach conservation with cultural sensitivity. Preservation efforts must involve collaboration with local communities, indigenous groups, and cultural custodians who hold invaluable knowledge about traditional practices and the historical importance of artifacts. By integrating this knowledge, conservators ensure that their techniques respect and enhance the artifact’s original context rather than inadvertently stripping it of meaning.
Embracing Indigenous Knowledge in Conservation
Indigenous knowledge systems offer invaluable insights into sustainable preservation practices. Passed down through generations, these methods often align with the environmental and social contexts in which artifacts exist. Integrating traditional conservation techniques into modern preservation efforts ensures that conservation strategies remain culturally relevant and ecologically responsible. For instance, the use of natural materials for repairs or adhering to specific rituals associated with artifact care can not only extend the life of these objects but also honor the traditions surrounding them.
The Role of Global Partnerships in Heritage Preservation
As threats to cultural heritage grow more complex, international collaboration becomes crucial. Organizations such as UNESCO and the International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS) play pivotal roles in fostering partnerships across borders, ensuring that expertise, resources, and strategies are shared among nations. These initiatives amplify conservation efforts, promote best practices, and reinforce the notion that cultural preservation is a global responsibility. By working together, countries can safeguard irreplaceable artifacts and structures, preserving the richness of human history for future generations.
Adapting to Environmental Challenges in Conservation
Climate change presents one of the most pressing dilemmas for cultural heritage conservation. Rising sea levels, flooding, wildfires, and extreme weather events threaten the physical integrity of countless artifacts and historical sites. To combat these risks, conservation techniques must evolve to address specific vulnerabilities. Outdoor sculptures, for example, may require protective coatings or physical barriers to mitigate damage, while delicate textiles may need climate-controlled storage to prevent deterioration. Through adaptive management strategies, conservators can create flexible, forward-thinking solutions that protect cultural heritage in an era of rapid environmental change.
Digital Preservation: A Modern Approach to Safeguarding History
Advancements in technology have revolutionized cultural heritage preservation. Digital archiving, 3D scanning, and virtual reality reconstructions enable artifacts to be preserved and studied without the risk of physical degradation. These technologies expand public access to cultural heritage, allowing global audiences to explore artifacts and historical sites remotely. However, digital preservation should complement rather than replace traditional conservation methods, ensuring that the tangible authenticity of artifacts remains intact. By striking a balance between technology and traditional preservation, conservators can create dynamic and accessible records of cultural heritage.
Promoting Intercultural Dialogue Through Preservation
Cultural heritage preservation is not just about protecting objects; it is also about fostering intercultural dialogue and understanding. By engaging with history and traditions through conservation efforts, communities create opportunities for meaningful exchange. In a world where cultural identities are increasingly fluid, these exchanges help cultivate a deeper appreciation for diversity. Preservation efforts thus become tools for bridging cultural divides, strengthening global connections, and reinforcing the importance of shared histories.
The Future of Cultural Heritage Conservation
Looking ahead, the future of cultural heritage conservation will depend on adaptability and responsiveness to emerging challenges and opportunities. Conservationists must integrate technological advancements, sustainable practices, and community engagement to create holistic preservation strategies. As artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and new restoration materials emerge, conservators must ensure these innovations align with ethical preservation standards and respect for cultural traditions.
A Shared Responsibility to Protect Our Heritage
Preserving cultural heritage is not just a technical endeavor; it is a collective responsibility that requires collaboration, respect, and understanding. By tailoring conservation techniques to the specific needs of each artifact and its cultural significance, we can ensure that our shared history remains intact for future generations. Embracing diverse knowledge systems, fostering global partnerships, and integrating technology into preservation efforts will allow us to safeguard cultural artifacts while honoring the stories they carry. As we confront the urgency of cultural heritage preservation, we must recognize that protecting these artifacts is more than an act of conservation, it is a commitment to maintaining the rich tapestry of human experience for centuries to come.