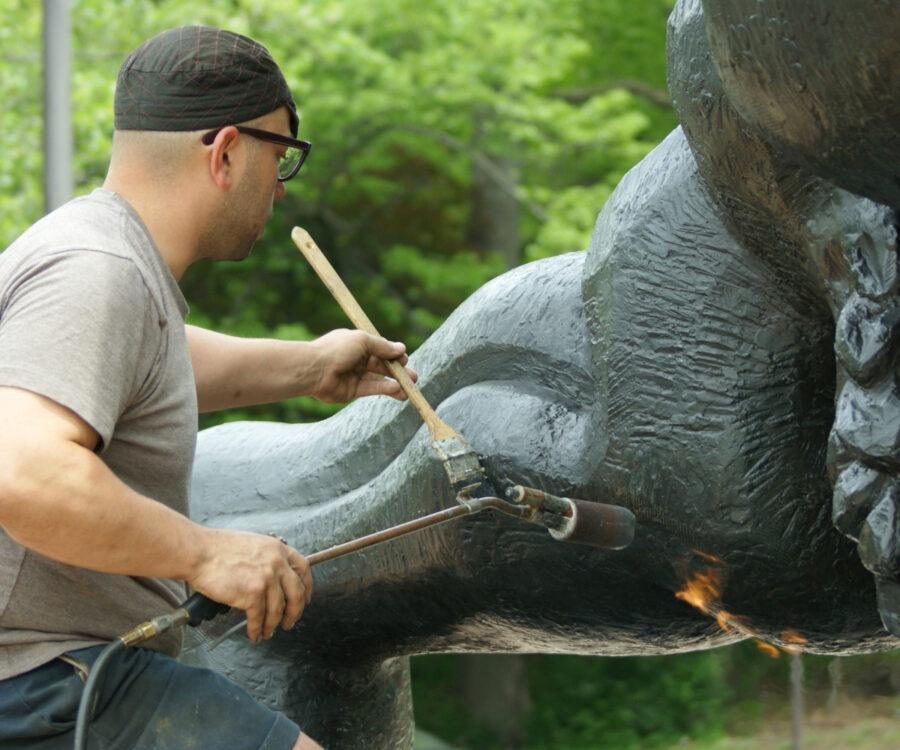
The conservation of outdoor sculpture is a discipline that seamlessly merges artistry and science. Unlike indoor artworks that benefit from controlled environments, outdoor sculptures are perpetually exposed to the elements, making their preservation uniquely challenging. Without proper care, these pieces of cultural heritage can rapidly deteriorate, losing their artistic and historical significance. As public art continues to thrive in urban landscapes, the demand for effective conservation methods has never been more urgent.
The Elements at Play: Environmental Risks to Outdoor Sculpture
Outdoor sculptures endure a host of environmental threats that can compromise their structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. Constant exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation can lead to discoloration, while moisture accelerates corrosion, mold growth, and material breakdown. Temperature fluctuations cause expansion and contraction, stressing the materials and leading to cracks or fractures. Additionally, pollution, especially in urban settings, introduces harmful particles that embed into surfaces, wearing them down over time.
Materials play a crucial role in determining a sculpture’s vulnerability. Metal sculptures, for example, are highly susceptible to rust and oxidation, while stone sculptures may erode due to acid rain and water infiltration. Wood sculptures, though less common in outdoor installations, face risks of rot, insect infestation, and warping. Each of these factors necessitates a tailored conservation strategy that accounts for the unique properties of the materials used in a sculpture’s construction.
Proactive Maintenance Strategies: Preserving Outdoor Artworks
An effective conservation strategy begins with proactive maintenance. Regular inspections are essential for detecting early signs of wear and damage, allowing conservators to intervene before issues escalate. Routine maintenance includes:
Cleaning: Removing dirt, pollutants, and biological growth to prevent long-term damage.
Protective Treatments: Applying coatings and sealants that guard against UV exposure, moisture, and chemical pollutants.
Structural Reinforcements: Addressing weakened areas through stabilization techniques such as resin infusions or metal support systems.
By implementing these preventive measures, conservators can significantly extend the lifespan of outdoor sculptures, preserving their original beauty and artistic intent.
Collaboration with Artists: Honoring Original Vision
Engaging with the original artists during the conservation process is an invaluable practice. Artists provide critical insights into the materials, techniques, and conceptual intentions behind their works, ensuring that any conservation efforts remain true to the original vision. When direct consultation is not possible, thorough documentation, including artist interviews, material analysis, and archival research, helps guide restoration efforts.
Such collaboration not only maintains the artistic integrity of sculptures but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the craftsmanship involved in their creation. By respecting the artist’s vision, conservation efforts ensure that restored sculptures retain their authenticity and cultural significance.
Community Engagement: Encouraging Public Participation in Preservation
Public art holds deep cultural and historical value, making community involvement an essential aspect of conservation. By raising awareness and educating the public about the importance of preserving outdoor sculptures, conservationists can foster a collective sense of responsibility. Community engagement efforts include:
Educational Workshops: Teaching citizens about proper maintenance techniques and the impact of environmental damage.
Volunteer Programs: Encouraging local participation in routine cleaning and preservation projects.
Public Art Tours: Highlighting the significance of sculptures and the efforts behind their conservation.
Through these initiatives, communities develop a stronger connection to public art, increasing their investment in its long-term preservation.
Technological Innovations: Advancing Conservation Practices
The integration of cutting-edge technology has revolutionized the field of outdoor sculpture conservation. Advanced imaging techniques, such as 3D scanning and photogrammetry, allow conservators to create detailed digital records of sculptures. These records serve as valuable references for future restoration work, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
Additionally, advancements in conservation materials have led to the development of environmentally friendly cleaning agents, corrosion inhibitors, and protective coatings. These innovative solutions not only extend the lifespan of sculptures but also align with contemporary sustainability efforts, reducing the ecological footprint of conservation practices.
The Importance of Cultural Heritage: Why Preservation Matters
Outdoor sculptures are more than artistic expressions; they are cultural landmarks that reflect societal values, historical narratives, and communal identities. Their presence in public spaces enriches urban environments, offering aesthetic, educational, and social benefits. By investing in the conservation of these sculptures, we reaffirm our commitment to cultural heritage and ensure that future generations can engage with these artistic legacies.
As cities continue to evolve, the role of public art becomes increasingly significant in maintaining a sense of historical continuity. Preserving outdoor sculptures safeguards not only the physical artifacts but also the stories, emotions, and cultural connections they represent.
A Future of Preservation: Ensuring Longevity for Outdoor Art
The conservation of outdoor sculpture is a multifaceted endeavor that requires technical expertise, collaborative efforts, and public engagement. As conservators navigate the complex challenges posed by environmental exposure, their work plays a crucial role in protecting cultural artifacts for posterity. By embracing innovative preservation techniques, fostering artist involvement, and encouraging community participation, we can ensure that outdoor sculptures remain integral parts of our shared landscapes. Moving forward, a commitment to sustainable conservation practices and interdisciplinary collaboration will be key to maintaining the vibrancy and significance of public art. In doing so, we honor not only the sculptures themselves but also the rich cultural heritage they embody.